you position:Home > us stock market today live cha > us stock market today live cha
Understanding US GAAP Accounting for Investments in Stocks
![]() myandytime2026-01-20【us stock market today live cha】view
myandytime2026-01-20【us stock market today live cha】view
info:
In the ever-evolving world of finance, understanding the nuances of accounting standards is crucial for investors and financial professionals alike. One such standard is the U.S. Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (US GAAP), which plays a pivotal role in the valuation and reporting of investments in stocks. This article delves into the intricacies of US GAAP accounting for investments in stocks, providing a comprehensive guide for those navigating the complexities of financial reporting.
What is US GAAP?
US GAAP is a set of accounting standards established by the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB). These standards are designed to provide a consistent framework for financial reporting, ensuring transparency and comparability across different companies and industries. For investors, understanding these principles is essential for making informed decisions about their investments.
Investments in Stocks: A Closer Look
When it comes to investments in stocks, US GAAP provides specific guidelines for how these assets should be accounted for. Here’s a breakdown of the key aspects:
1. Initial Recognition and Measurement
Under US GAAP, investments in stocks are initially recognized at cost. This cost includes the purchase price of the stock, as well as any directly attributable costs, such as brokerage fees. However, the subsequent measurement of these investments can vary depending on the classification.
2. Fair Value Measurement
Investments in stocks can be classified into three categories: trading securities, available-for-sale securities, and held-to-maturity securities. Each category has different measurement requirements:
- Trading Securities: These are investments bought and held primarily for sale in the near term. They are measured at fair value, with changes in fair value recognized in the income statement.
- Available-for-Sale Securities: These are investments that are not classified as trading securities or held-to-maturity securities. They are also measured at fair value, but changes in fair value are recognized in other comprehensive income (OCI) and reclassified to the income statement at the time of sale.
- Held-to-Maturity Securities: These are investments that the entity has the positive intention and ability to hold to maturity. They are initially measured at cost and are adjusted for amortized cost, which includes interest income and impairment losses.
3. Impairment Testing
US GAAP requires entities to perform impairment testing on their investments in stocks at each reporting date. If the fair value of an investment falls below its carrying amount, an impairment loss is recognized in the income statement.
Case Study: XYZ Corporation
Let’s consider a hypothetical case involving XYZ Corporation, which has invested in a diversified portfolio of stocks. At the end of the fiscal year, XYZ Corporation performs impairment testing on its investments and discovers that the fair value of one of its stocks has fallen below its carrying amount. As a result, XYZ Corporation recognizes an impairment loss in its income statement, which negatively impacts its financial performance.
Conclusion
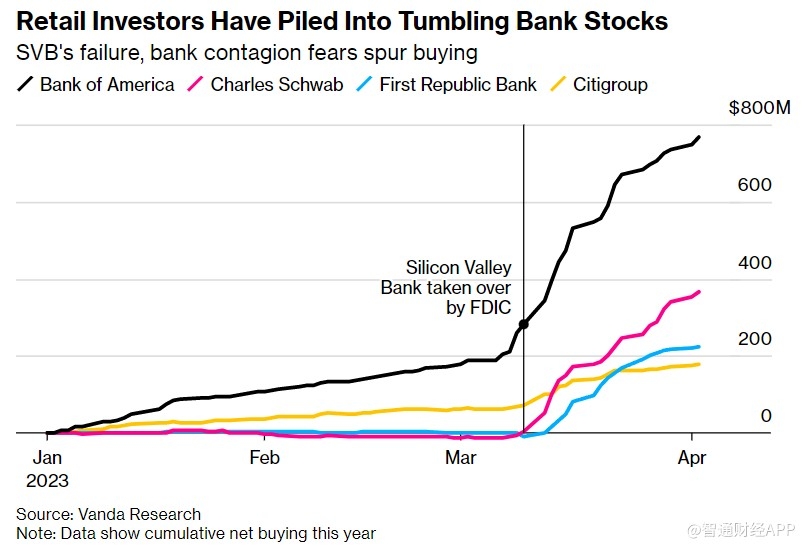
Understanding US GAAP accounting for investments in stocks is essential for investors and financial professionals. By following these guidelines, entities can ensure accurate and transparent financial reporting, enabling stakeholders to make informed decisions. As the financial landscape continues to evolve, staying abreast of these accounting principles is crucial for success in the investment world.
so cool! ()
last:TCS US Stock Price: A Comprehensive Analysis
next:nothing
like
- TCS US Stock Price: A Comprehensive Analysis
- US Gas Company Stock: The Ultimate Guide to Investment Opportunities
- TLRY Us Stock: The Ultimate Guide to Investing in American Stocks
- US Senator Sells Stock: The Truth Behind the Transactions"
- US Stock Index Investing: A Comprehensive Guide on Investopedia
- Understanding the US Stock Market: A Comprehensive Bar Chart Analysis
- Current US Stock Market Valuation: A Comprehensive Look at June 2025
- The Cheapest Way to Buy US Stocks in the UK: A Comprehensive Guide
- Top US Stocks Drawdowns 1985-2024: A Comprehensive Analysis
- U.S. Company in Stock: Ready to Ship Your Next Order
- US Stock Exchange Holiday Schedule: Comprehensive Guide
- Can You Trade Us Stocks on Wealthsimple? A Comprehensive Guide
hot stocks
 HBHarat Electronic Stock on US Market: A Compr
HBHarat Electronic Stock on US Market: A Compr- HBHarat Electronic Stock on US Market: A Compr"
- Best Performing Large Cap US Stocks This Week:"
- US Stock Futures Rise Amid Government Shutdown"
- June 8, 2025: US Stock Market Summary"
- US Passport and Shell Stock Photo High Resolut"
- PS5 Stock Update: What You Need to Know in the"
- US Refineries Stocks: A Comprehensive Guide to"
- Title: Understanding the Real Return on Your I"
recommend
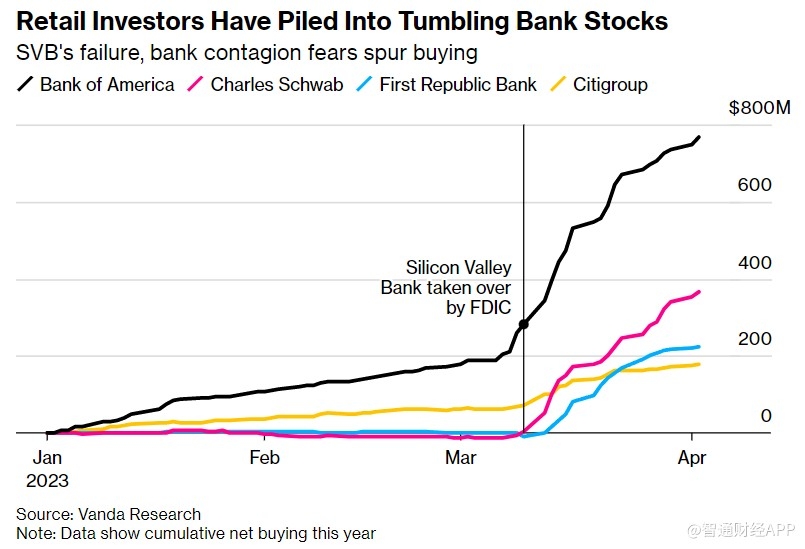 Understanding US GAAP Accounting for Investmen
Understanding US GAAP Accounting for Investmen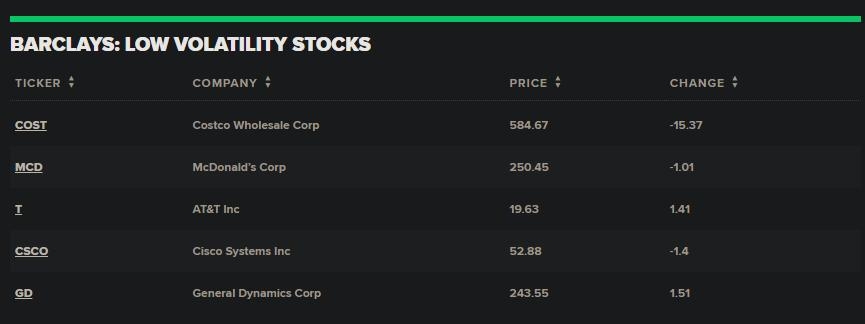
How to Invest in US Stocks from Singapore: A C

Samsung Galaxy Note 2 Stock ROM for US Cellula

US Stock Exchange Holiday Schedule: Comprehens
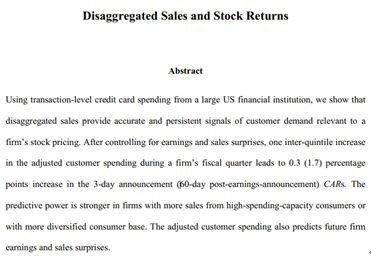
Tax Implications for US Citizens Investing in

HSBC Buys US Stock: A Strategic Move for Globa
Baillie Gifford US Growth Trust Stock: A Compr
HelloFresh US Stock Symbol: A Comprehensive Gu

Title: Tax Treatment of US Corporation Selling
Car Dealers in China: A US Stock Market Perspe

US Pot Stock: The Growing Market of Legal Cann
tags
-
TomorrowAprilFuturesRareGrowingUnderstaComprehensAllegedLNGExchangAcronymHolCanEssentialGoldClosedCannabisEarthPerExchange20182021IndianfromLo5130150NameTankAlternative4245GalChineseIslandStrategyPivotalDefinitioJonesDelhaizeManyA7IIISchwabCompletionMarCitizensFallEdibleMFCListDidNintendo2ndDaysNon-USBogleheOpenHolidaysBYDDelekSmallPurchaseRiskHighwaySixth-Gener2023LargestFoodTotal2019InsectAholdTimingstodshareShausaveruamerican10010miniliveAvnasdaqSustainaPharmaceCleaFuUnderaverage us stocks games silver etf us stock
like
- Title: ETF US Stocks: Your Ultimate Guide to I"
- Iron Ore Stocks US: A Comprehensive Guide to I"
- Market Outlook: October 2025 - U.S. Stocks to "
- Title: CIBC US Stock Price: A Comprehensive An"
- How to Buy US Stocks from Vietnam"
- Lumber Stocks: A Growing Industry in the US"
- US Stock Gainers & Losers: Analyzing M"
- Understanding the US Stock Estate Tax: A Compr"
- Top US Stock Movers Today: Insights into Marke"
- Unlocking the Potential of Stock Investment in"

