you position:Home > us stock market today > us stock market today
How CPI Affects the U.S. Stock Market
![]() myandytime2026-01-15【us stock market today live cha】view
myandytime2026-01-15【us stock market today live cha】view
info:
The Consumer Price Index (CPI) is a critical economic indicator that measures the average change over time in the prices paid by urban consumers for a market basket of consumer goods and services. Understanding how the CPI affects the U.S. stock market is crucial for investors and market analysts. This article delves into the relationship between CPI and the stock market, highlighting the key factors that influence this connection.
Inflation and Stock Market Performance
One of the primary ways in which the CPI affects the stock market is through its impact on inflation. Inflation refers to the rate at which the general level of prices for goods and services is rising, and subsequently, purchasing power is falling. When the CPI rises, it typically indicates higher inflation, which can have several effects on the stock market.
1. Corporate Profits
Higher inflation can lead to increased costs for businesses, including raw materials, labor, and energy. As a result, corporate profits may suffer, negatively impacting stock prices. Conversely, lower inflation can lead to higher profits, as businesses face lower costs, which can drive stock prices up.
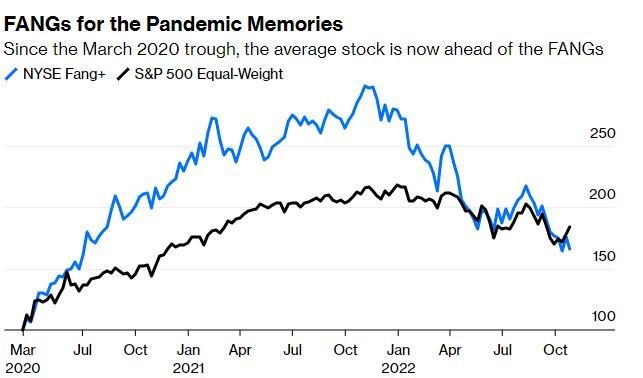
2. Interest Rates
The Federal Reserve uses the CPI to gauge inflation and make decisions about interest rates. When the CPI rises, the Federal Reserve may raise interest rates to combat inflation. Higher interest rates can make borrowing more expensive for businesses, leading to lower stock prices. Conversely, lower inflation and lower interest rates can stimulate economic growth and drive stock prices higher.
3. Consumer Spending
The CPI also reflects changes in consumer spending patterns. When the CPI rises, consumers may experience a decrease in purchasing power, leading to lower spending. This can negatively impact companies that rely heavily on consumer demand, potentially leading to lower stock prices. Conversely, lower inflation can lead to higher consumer spending, benefiting companies and potentially driving stock prices up.
Case Study: The 1970s Inflation
One notable example of the CPI's impact on the stock market is the inflationary period of the 1970s. During this time, the CPI rose significantly, leading to higher interest rates and increased corporate costs. As a result, stock prices fell, and the stock market experienced a period of volatility.
Dividend Yields and CPI
Another way in which the CPI affects the stock market is through its impact on dividend yields. Dividend yields are the percentage return on an investment in the form of dividends. When the CPI rises, the real value of dividends may decrease, leading to lower dividend yields. This can make stocks less attractive to investors, potentially leading to lower stock prices.
Conclusion
Understanding the relationship between the CPI and the U.S. stock market is essential for investors and market analysts. By monitoring the CPI, investors can gain insights into inflation trends, interest rates, and consumer spending patterns, which can help them make informed investment decisions. While the CPI is just one of many factors that influence the stock market, its impact cannot be overlooked. As the economy continues to evolve, staying informed about the CPI and its effects on the stock market will be crucial for investors seeking to navigate the complexities of the financial markets.
so cool! ()
last:US Large Cap Stocks: Best Performers in September 2024
next:nothing
like
- US Large Cap Stocks: Best Performers in September 2024
- Title: Current US and Europe Stock Market: Insights and Analysis
- http stocks.us.reuters.com stocks fulldescription.asp rpc 66&symbol hyh:
- Title: Top Marijuana Stocks in the US
- US Stock Market Alternatives: Exploring Diverse Investment Opportunities
- US Listed Pot Stocks: A Comprehensive Guide to the Legal Cannabis Market
- Title: "http stocks.us.reuters.com stocks ratios.asp rpc 66&symb
- Title: US Alliance Stock Price: A Comprehensive Analysis
- Title: "http stocks.us.reuters.com stocks fulldescription.asp rpc 66&
- How to Start Investing in the US Stock Market
- US Airport Stocks: A Flight Path to Profitability
- Title: US Marijuana Stocks Listed in Canada: A Comprehensive Guide
hot stocks
 When Does the US Stock Market Open?
When Does the US Stock Market Open?- US Rare Earth Stock: A Lucrative Investment Op"
- When Does the US Stock Market Open?"
- Pyrogenesis Stock US: A Deep Dive into Investm"
- Highest Dividend Yield Stocks in the US: Top P"
- Is the US Stock Market Open Today on Columbus "
- Infineon US Stock: A Comprehensive Analysis"
- US Listed Pot Stocks: A Comprehensive Guide to"
- Does Among Us Have Stock? A Comprehensive Guid"
recommend
 How CPI Affects the U.S. Stock Market
How CPI Affects the U.S. Stock Market
Cpg Us Stock: A Comprehensive Guide to Investi
How Many Trillions is the US Stock Market Wort

Title: US Foods Stock Yards Meat Buffalo NY 14
Best Cannabis Stocks to Buy for US Legalizatio

How to Start Investing in the US Stock Market

Title: Highest Dividend US Stocks: Your Guide

Palantir US Stock: A Deep Dive into the Data A
T-Mobile US to Give Away Stock to Customers: A
Emerging Meme Stocks in the US: October 2025 O

Current US Stock Market Valuation Metrics: CAP
tags
-
TomorrowAprilFuturesRareGrowingUnderstaComprehensAllegedLNGExchangAcronymHolCanEssentialGoldClosedCannabisEarthPerExchange20182021IndianfromLo5130150NameTankAlternative4245GalChineseIslandStrategyPivotalDefinitioJonesDelhaizeManyA7IIISchwabCompletionMarCitizensFallEdibleMFCListDidNintendo2ndDaysNon-USBogleheOpenHolidaysBYDDelekSmallPurchaseRiskHighwaySixth-Gener2023LargestFoodTotal2019InsectAholdTimingstodshareShausaveruamerican10010miniliveAvnasdaqSustainaPharmaceCleaFuUnderaverage us stocks games silver etf us stock
like
- Delek US Holdings Stock Price: A Comprehensive"
- Most Expensive US Stocks: A Closer Look at the"
- Fred and the U.S. Stock Market Volatility: Nav"
- Canadian Cannabis Traded in US Stock Market: A"
- Can I Buy Aston Martin Stock on the US Stock E"
- How to Buy MediaTek Stock in the US"
- Cpg Us Stock: A Comprehensive Guide to Investi"
- Novonix Stock US: A Comprehensive Analysis"
- Top Performing US Stocks Past 5 Days: Unveilin"
- Must Invest Stocks in US: Why Now is the Perfe"

