you position:Home > us stock market live > us stock market live
How Much Stock Does the U.S. Government Own?
![]() myandytime2026-01-17【us stock market today live cha】view
myandytime2026-01-17【us stock market today live cha】view
info:
The U.S. government's ownership of stocks is a topic that often sparks curiosity and debate. From investments in major corporations to its role in the stock market, the government's involvement is significant. In this article, we will delve into the extent of the U.S. government's stock ownership, its impact on the market, and the reasons behind this investment strategy.
Understanding the Scope of U.S. Government Stock Ownership
The U.S. government owns a substantial amount of stock across various sectors. This ownership is primarily through two main entities: the Federal Reserve and the U.S. Treasury. The Federal Reserve holds stocks in member banks, while the Treasury owns stocks as part of its investment portfolio.
The Federal Reserve's stock ownership is unique because it is not like traditional stock ownership. Member banks own shares of the Federal Reserve, and these shares do not represent equity ownership. Instead, they serve as a form of capital for the Federal Reserve System. The interest on these shares is paid to the member banks, and the profits from the Federal Reserve's operations are returned to the U.S. Treasury.
The U.S. Treasury's stock ownership is more straightforward. It invests in a diversified portfolio of stocks, bonds, and other securities. This investment strategy is aimed at maximizing returns while managing risk.
Impact on the Stock Market
The U.S. government's stock ownership has a significant impact on the stock market. With billions of dollars invested in various companies, the government's actions can influence stock prices and market trends.
When the government buys stocks, it can drive up demand and potentially increase prices. Conversely, when it sells stocks, it can create a surplus of shares and potentially drive down prices. This dynamic can lead to volatility in the market, especially during times of economic uncertainty.
Reasons for Government Stock Ownership
The U.S. government's investment in stocks serves several purposes:
Economic Stabilization: By owning stocks, the government can help stabilize the economy during times of crisis. For example, during the 2008 financial crisis, the government invested billions of dollars in major banks to prevent a collapse.
Return on Investment: The government's investment in stocks is aimed at generating returns. These returns can be used to fund government programs and reduce the national debt.
Market Influence: The government's ownership of stocks allows it to exert influence on the market. This influence can be used to promote economic growth and stability.
Case Studies
One notable example of the government's stock ownership is the Troubled Asset Relief Program (TARP). Implemented during the 2008 financial crisis, TARP provided billions of dollars to struggling banks and financial institutions. In return, the government received stock in these companies. Over time, the government sold these stocks, recouping its investment and even generating a profit.
Another example is the government's investment in the General Motors Corporation. During the 2009 financial crisis, the government provided a substantial bailout to GM, which included stock ownership. By 2010, the government sold its remaining shares, recouping its investment and even making a profit.
Conclusion
The U.S. government's ownership of stocks is a complex and multifaceted issue. While it has the potential to influence the stock market, its primary goal is to generate returns and stabilize the economy. Understanding the scope and impact of this ownership is crucial for anyone interested in the U.S. government's role in the stock market.
so cool! ()
last:Cheap US Bank Stocks: Smart Investments for Savvy Investors
next:nothing
like
- Cheap US Bank Stocks: Smart Investments for Savvy Investors
- Title: Minimum Lot Size for US Stocks: What You Need to Know
- Continental Stock Transfer and Trust: Your Ultimate Toll-Free Resource for Secure
- US Holidays 2021 Stock Market: Impact and Insights
- Title: Dyson Stock US: A Deep Dive into the World of Innovation and Financial Suc
- Title: Top Momentum US Stocks September 2025
- Free Stock: Contact Us for Unbeatable Media Assets
- Should I Invest in US Stocks from India?
- Title: "http stocks.us.reuters.com stocks fulldescription.asp rpc 66&
- Title: "US Stock Market 50 Years: A Look Back at Decades of Growth and I
- Title: US Large Cap Stocks with Low PE Ratio: Value Stocks to Watch
- Title: Today's US Stock Market Position: Insights and Analysis
hot stocks
 Indivior Stock in US Dollars: A Comprehensive
Indivior Stock in US Dollars: A Comprehensive - Indivior Stock in US Dollars: A Comprehensive "
- Title: US Government Shutdown: The Impact on t"
- Title: "ADAR 2-15: Why Buying Stock i"
- How to Buy Stock Outside the US: A Comprehensi"
- Lly Us Stock: Unlocking the Potential of Stock"
- Title: Best Non-US Dividend Stocks to Invest I"
- Kraken Launches Commission-Free Trading of US "
- US Stock Exchange Holiday List 2018: A Compreh"
recommend
 How Much Stock Does the U.S. Government Own?
How Much Stock Does the U.S. Government Own?
Title: TFSA Buy US Stocks: A Guide for Canadia
US Publicly Traded Pot Stocks: A Comprehensive
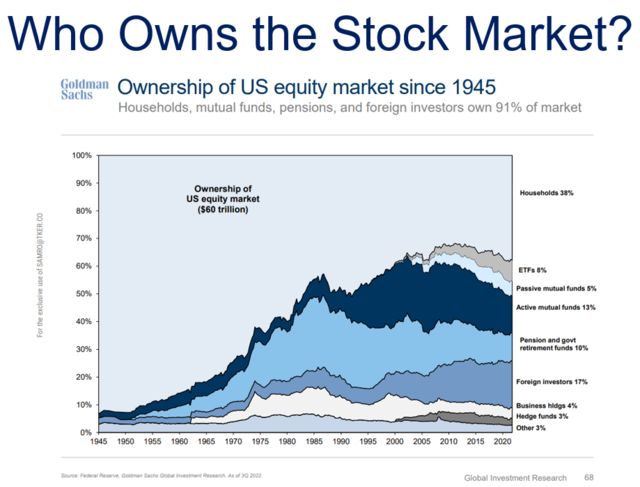
Understanding the US Clothing Stock Market Log

Can I Buy Baidu Stock in the US? A Comprehensi

US Fusion Energy Stocks Companies: The Future

US Steel Stock: A Comprehensive Yahoo Finance
Title: US Stock Investment App: Revolutionizin
August 19, 2025: US Stock Market Summary
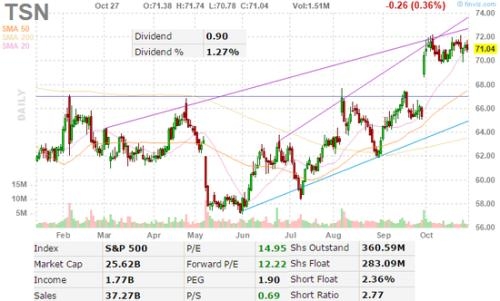
Title: Toys "R" Us Stock in
US Housing Stock Value: Understanding the Curr
tags
-
TomorrowAprilFuturesRareGrowingUnderstaComprehensAllegedLNGExchangAcronymHolCanEssentialGoldClosedCannabisEarthPerExchange20182021IndianfromLo5130150NameTankAlternative4245GalChineseIslandStrategyPivotalDefinitioJonesDelhaizeManyA7IIISchwabCompletionMarCitizensFallEdibleMFCListDidNintendo2ndDaysNon-USBogleheOpenHolidaysBYDDelekSmallPurchaseRiskHighwaySixth-Gener2023LargestFoodTotal2019InsectAholdTimingstodshareShausaveruamerican10010miniliveAvnasdaqSustainaPharmaceCleaFuUnderaverage us stocks games silver etf us stock
like
- Title: Does the U.S. Military Protect Us Stock"
- The Most Expensive Publicly Traded Stock in th"
- Understanding US Steel Preferred Stock: A Comp"
- US Steel Stock Cut in Half with Layoffs: The I"
- Free Stock: Contact Us for Unbeatable Media As"
- ASX US Stock: Understanding the Intersection o"
- Strong US Stocks Outlook 2025: What Investors "
- Title: FTSE 100 vs US Growth Stocks: A Compreh"
- Title: Stock Price for US Robotics: What You N"
- Us Food Stocks: The Essential Guide to America"

