you position:Home > aphria us stock > aphria us stock
Tax on US Stocks: Understanding the Implications and Strategies"
![]() myandytime2026-01-23【us stock market today live cha】view
myandytime2026-01-23【us stock market today live cha】view
info:
Introduction:
In the world of investing, understanding the tax implications is crucial. One of the key aspects investors need to consider is the tax on US stocks. This article delves into the details of this tax, its implications, and strategies to optimize your investments. Whether you are a seasoned investor or just starting out, this guide will provide you with valuable insights into the tax on US stocks.
Understanding the Tax on US Stocks:
The tax on US stocks primarily refers to the capital gains tax. This tax is imposed on the profit you make when selling stocks that you've held for more than a year. The rate at which you are taxed depends on your income level and the type of stock you are selling.
Short-term capital gains, which are profits from stocks held for less than a year, are taxed as ordinary income. This means they are subject to your regular income tax rate. On the other hand, long-term capital gains are taxed at a lower rate, ranging from 0% to 20%, depending on your taxable income.
Key Factors Affecting the Tax on US Stocks:
Holding Period: As mentioned earlier, the tax rate differs based on the holding period of the stock. Holding stocks for more than a year qualifies them for long-term capital gains treatment, offering lower tax rates.
Tax Bracket: Your income level determines the tax rate you'll pay on your capital gains. The lower your income, the lower the tax rate. Conversely, higher-income investors may face higher capital gains tax rates.
Type of Stock: Different types of stocks, such as stocks, bonds, and mutual funds, may have different tax implications. Understanding the specific tax treatment of each type is essential.
Strategies to Optimize Your Tax on US Stocks:
Tax-Loss Harvesting: This strategy involves selling stocks that have declined in value to offset capital gains taxes. By doing so, you can reduce your overall tax liability.
Utilize Tax-Deferred Accounts: Consider investing in tax-deferred accounts like IRAs or 401(k)s. These accounts allow you to defer taxes on capital gains until you withdraw the funds, potentially reducing your tax burden.
Diversify Your Portfolio: Diversifying your portfolio can help reduce your exposure to specific stock taxes. By investing in various asset classes, you can spread out the tax implications and minimize the impact of capital gains taxes.
Consider Long-Term Investments: Investing in stocks with a long-term perspective can help you benefit from lower tax rates on long-term capital gains.

Case Study:
Let's consider a hypothetical scenario. John, a high-income earner, invested in a tech stock and held it for less than a year. Upon selling the stock, he realized a significant profit. However, since the stock was held for less than a year, the profit would be taxed as ordinary income, resulting in a higher tax rate.
Alternatively, if John had held the same stock for more than a year, the profit would be taxed at a lower long-term capital gains rate. By understanding the tax implications and strategically holding his investments, John could have minimized his tax liability.
Conclusion:
Understanding the tax on US stocks is crucial for investors to optimize their investments and minimize their tax burden. By considering factors like holding period, tax bracket, and type of stock, investors can develop effective strategies to manage their tax liability. Remember, seeking professional advice from a financial advisor or tax professional is always recommended to ensure compliance with tax regulations and maximize your investment returns.
so cool! ()
last:Is NYSE Open Now? The Ultimate Guide to the Stock Market's Hours
next:nothing
like
- Is NYSE Open Now? The Ultimate Guide to the Stock Market's Hours
- SP500 Record High: A Deep Dive into the Market's Milestone
- Unlocking the Power of Markets Finance: A Comprehensive Guide
- Top 10 US Stocks to Invest In: A Comprehensive Guide"
- Signal Us Stock: The Ultimate Guide to Stock Alerts and Notifications
- Best App to Track Stock Market: Unveiling the Ultimate Investment Tool
- US Rare Earth Stock News: Market Trends and Investment Insights
- Stock Market Prediction Next Month: What to Expect and How to Prepare
- Is the Dow Open Today? A Comprehensive Guide to Today's Market Status
- Receiving Stock from a Non-US Person: A Comprehensive Guide
- Buckeye Partners Stock: A Comprehensive Guide to Investing in US Energy Infrastru
- Biggest Movers Stock Today: Unveiling the Market's Top Performers
recommend
 Tax on US Stocks: Understanding the Implicatio
Tax on US Stocks: Understanding the Implicatio
Global Stocks Slip as US-China Tensions Add to
http stocks.us.reuters.com stocks fulldescript
Unlocking Opportunities in AmerisourceBergen U
Best US Stocks to Watch in 2019: Top Picks for

Multibagger US Stocks: Unveiling the Power of
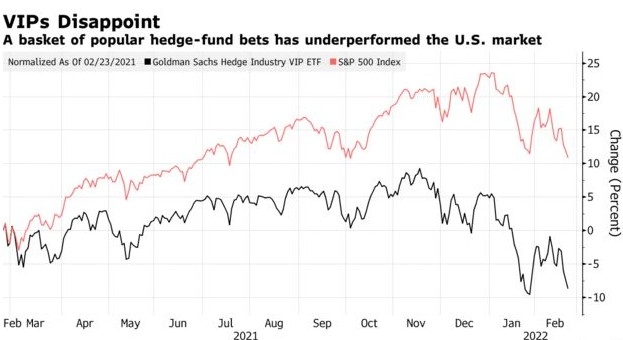
Jim Rogers Sold All US Stocks: What It Means f
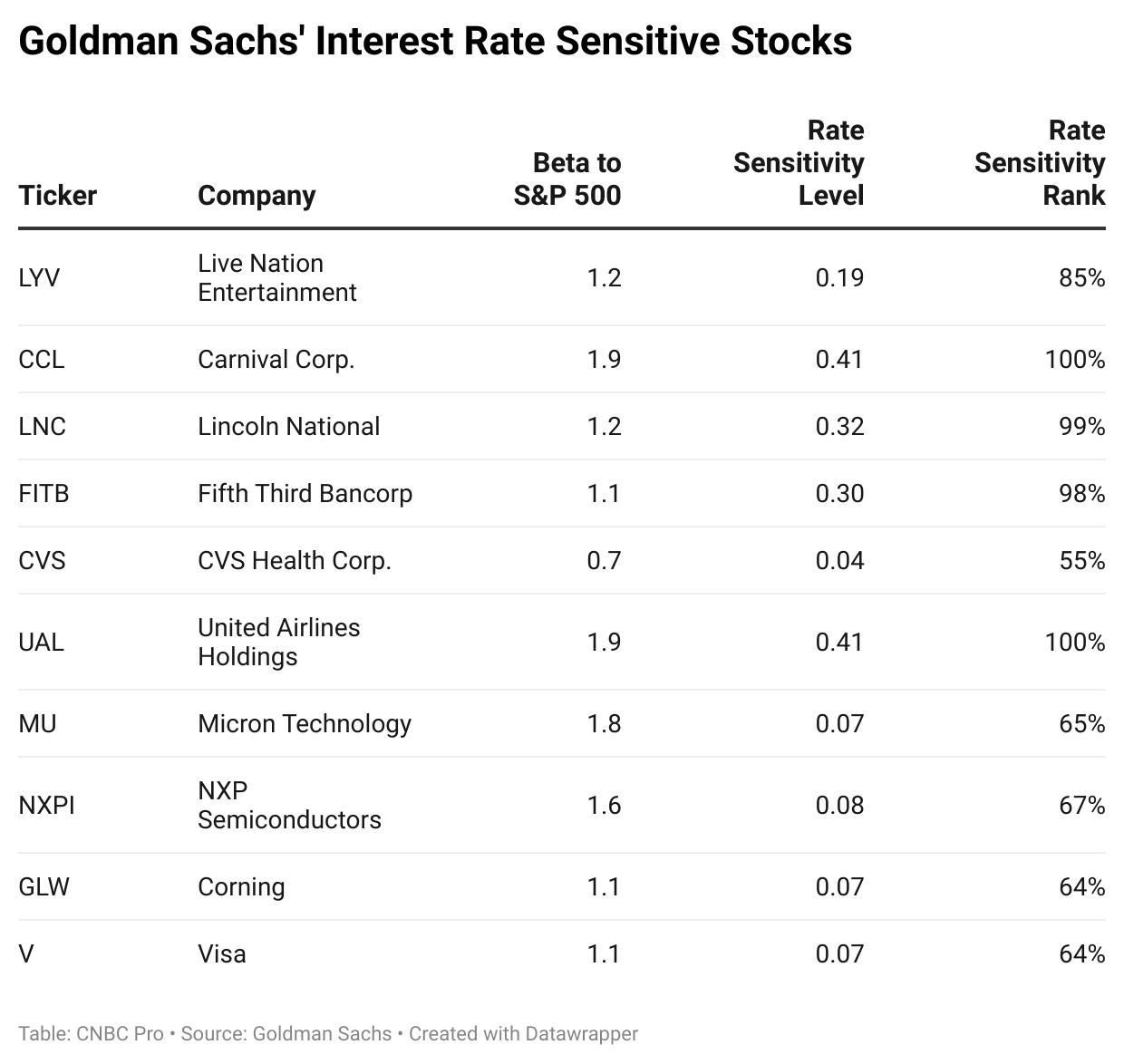
How Did the US Stock Market Close Yesterday? A

Met Us Stock: Discover the Ultimate Investment
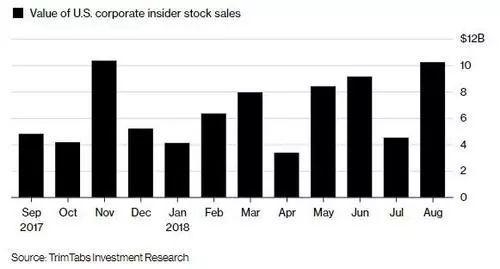
US Presidents and Stock Market Performance: A
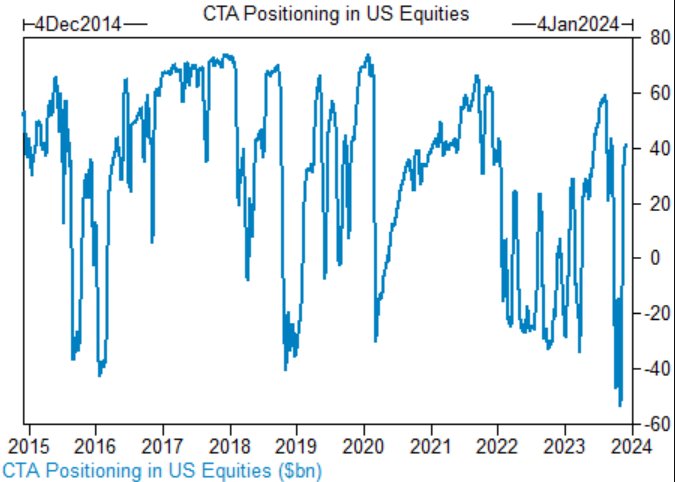
Unlocking Investment Opportunities: Exploring
tags
-
WeightJunPoxCRSPKiaMonetaryCatalystsPlungeBankingWikiE6603BeneficiarieSalarMisstepComparElectiHarnesRPCCampaignBBCOTUnsoldNastiticPractiseRidePFContinuesBoughtAnnuHigRoughAdaroStocks-USSorosNorthernMcMillanEvenMaricannltcgCROL.SolarWorldStock.InvestAnimeDaiTriangleDynastyParallelsContractorsCSVTreBermudaTransactionIn-GrowerManitexVetPlansBrManchesterPositionsBeefWeightingBuybacAetnawitShareholdeProminentMaximizeResidSSNOftenCouldTDWPremiumShoSPACYumRisinLivestockWarnChangerSalsusETST.PKRaytheonSYRG.KOriginSberJPMorganAPICloud us stocks us stock games silver etf
like
- Best US Stocks for Short-Term Trading: Unveili"
- Niu US Stock: A Comprehensive Guide to Investi"
- options trading strategies"
- US Copper Stocks List: Your Ultimate Guide to "
- Lithium Mining Stocks: A Lucrative Investment "
- Understanding the US Housing Stock Turnover: A"
- stock market forecast 2025"
- Unlocking the Potential: Understanding US Empl"
- Global Stocks Slip as US-China Tensions Add to"
- Title: US Insurance Companies Stocks: A Compre"